目录
一.5G 协议数据包封装的用途
二.协议数据包封装的原理
1.数据字段的划分
2.序列化
3.网络字节序的转换
4.封装协议的定义
5.反序列化
6.校验和计算
三.5G协议数据包封装类代码实现
四.总结
一.5G 协议数据包封装的用途
协议数据包封装的目的是确保在不同的系统、设备和网络节点之间,数据可以按照一致的格式传输和解析。
1.数据传输和通信:在 5G 网络中,数据传输是通过标准化的数据包格式进行的,数据包封装将数据按规定的格式打包,确保数据能够通过网络正确传输。
2.协议的标准化和一致性:5G 协议数据包封装为不同的设备和网络节点提供了统一的数据格式,使得无论是终端、基站,还是核心网络都可以理解和处理数据包。
3.数据包的完整性校验:封装过程中,除了包含数据外,还会计算校验和,确保数据在传输过程中没有发生损坏或篡改。接收端可以根据校验和检查数据包是否完整。
4.提升传输效率与网络安全:数据包封装不仅包含数据,还包含控制信息(如数据包的标识符、序列号等)。这些信息帮助接收端处理不同类型的数据,并支持数据的顺序恢复、错误检查和数据包重传,提升了网络效率和安全性。
5.分段和重组:如果数据过大,不能一次性传输,协议数据包封装能够将数据分割成多个小的数据包进行传输。接收端再根据协议进行重组,确保完整数据的恢复。
二.协议数据包封装的原理
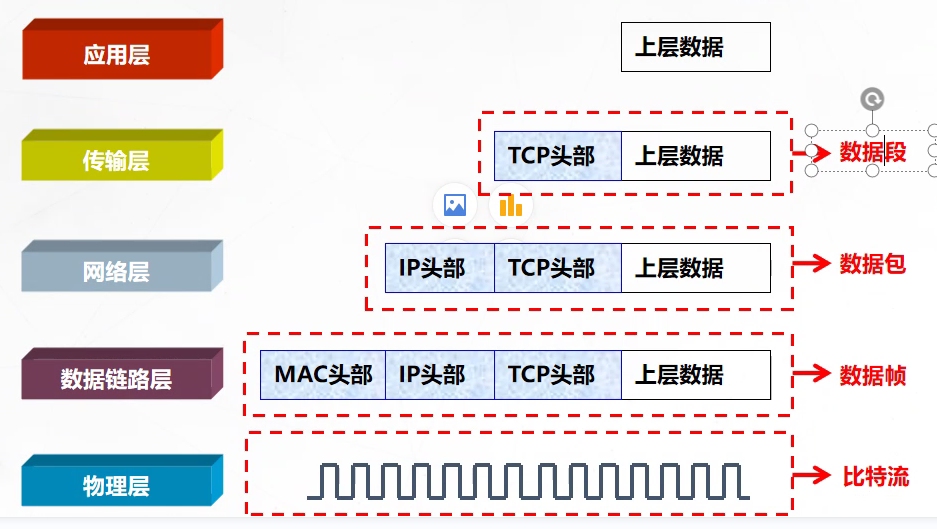
这张图片展示了一个典型的 OSI七层模型(开放系统互联参考模型)的图示,其中每一层都有不同的功能和数据处理方式。可以看到,图中标出了从 应用层 到 物理层 的数据处理过程,并且展示了不同层级的数据包如何通过传输过程在物理媒介中传输。
应用层(Application Layer):在上层数据产生后,数据会先进入应用层,通常表示用户的应用程序生成的数据,如 HTTP 请求数据或用户输入数据。
传输层(Transport Layer):在传输层,数据包会被加入TCP、UDP等传输层协议的头部信息,如端口号、序列号等,这对应了我们5G协议数据包中的 包类型 和 时间戳 信息。
网络层(Network Layer):在网络层,数据包会包含 IP 头部信息,其中包括目标IP地址,这与协议数据包封装中的 协议版本 和 包类型 相似。
数据链路层(Data Link Layer):在数据链路层,数据包会加入 MAC 地址等信息(如MAC头部),并准备进行物理层的传输。对应的 5G 数据包中的载荷和校验和部分。
物理层(Physical Layer):最后,在物理层,数据被转换为电信号或光信号,通过物理媒介(如电缆或无线信号)进行传输。
1.数据字段的划分:
每个协议数据包由多个字段组成,典型的字段包括:
协议版本(Protocol Version):表示数据包遵循的协议版本。
包类型(Packet Type):标识数据包的类型,如控制信息包、数据包等。
时间戳(Timestamp):记录数据包生成的时间,通常是一个 64 位的整数(例如 Unix 时间戳)。
载荷(Payload):包含实际的数据内容,这通常是传输的用户数据、请求、响应等。
校验和(Checksum):用于检测数据是否在传输过程中发生损坏或篡改。
2.序列化:
- 序列化(Serialization)是将数据结构(如类、对象等)转换为字节流的过程。协议数据包封装类会将各个字段的数据按协议要求的格式组织起来并序列化,转换为一个字节流(std::vector<uint8_t>)。这个字节流可以通过网络或存储设备进行传输。
3.网络字节序的转换:
- 网络通信中使用的是 大端字节序(Big Endian),而不同的计算机可能使用不同的字节序(如小端字节序)。为了确保数据在不同系统间传输时不会出错,协议数据包封装类会进行 字节序转换,将数据按照大端字节序(网络字节序)进行排列。
4.封装协议的定义:
- 协议数据包的结构(如协议版本、包类型、载荷等)是根据特定通信协议来定义的。比如在 5G 网络中,可能会有不同类型的数据包,每种数据包的字段结构可能不同,因此需要定义一个符合协议的数据包封装类,确保每个字段的正确处理。
5.反序列化:
- 反序列化(Deserialization)是将字节流恢复成原始数据结构的过程。当接收方接收到序列化的数据包时,它会根据协议的定义,反序列化字节流,恢复出数据包的各个字段(协议版本、包类型、载荷等)。
6.校验和计算:
- 在数据包中加入 校验和(Checksum),用于在接收端校验数据是否正确。如果数据包在传输过程中发生了错误或损坏,校验和验证将失败,接收方会丢弃该数据包或请求重传。
三.5G协议数据包封装类代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdint>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <stdexcept>
#ifdef _WIN32
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <ws2tcpip.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "Ws2_32.lib")
#else
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#endif
class FiveGDataPacket
{
private:
uint8_t protocol_version;
uint8_t packet_type;
uint64_t timestamp;
std::vector<uint8_t> payload;
uint32_t checksum;
void calculate_checksum()
{
checksum = std::accumulate(payload.begin(), payload.end(), 0);
}
public:
explicit FiveGDataPacket(uint8_t ver = 1, uint8_t type = 0, uint64_t ts = 0, const std::vector<uint8_t>& data = {})
: protocol_version(ver),
packet_type(type),
timestamp(ts),
payload(data)
{
calculate_checksum();
}
FiveGDataPacket(const FiveGDataPacket& other) = default;
FiveGDataPacket(FiveGDataPacket&& other) noexcept = default;
FiveGDataPacket& operator=(const FiveGDataPacket& other) = default;
bool operator==(const FiveGDataPacket& other) const
{
return (protocol_version == other.protocol_version) &&
(packet_type == other.packet_type) &&
(timestamp == other.timestamp) &&
(payload == other.payload) &&
(checksum == other.checksum);
}
std::vector<uint8_t> serialize() const
{
std::vector<uint8_t> buffer;
buffer.push_back(protocol_version);
buffer.push_back(packet_type);
uint64_t net_timestamp = htonll(timestamp);
auto ts_ptr = reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(&net_timestamp);
buffer.insert(buffer.end(), ts_ptr, ts_ptr + 8);
uint16_t payload_length = static_cast<uint16_t>(payload.size());
uint16_t net_payload_len = htons(payload_length);
auto len_ptr = reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(&net_payload_len);
buffer.insert(buffer.end(), len_ptr, len_ptr + 2);
buffer.insert(buffer.end(), payload.begin(), payload.end());
uint32_t net_checksum = htonl(checksum);
auto cs_ptr = reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(&net_checksum);
buffer.insert(buffer.end(), cs_ptr, cs_ptr + 4);
return buffer;
}
static FiveGDataPacket deserialize(const std::vector<uint8_t>& buffer)
{
if (buffer.size() < 16) {
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid packet format");
}
FiveGDataPacket packet;
size_t pos = 0;
packet.protocol_version = buffer[pos++];
packet.packet_type = buffer[pos++];
uint64_t net_timestamp;
std::copy(buffer.begin() + pos, buffer.begin() + pos + 8,
reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(&net_timestamp));
packet.timestamp = ntohll(net_timestamp);
pos += 8;
uint16_t net_payload_len;
std::copy(buffer.begin() + pos, buffer.begin() + pos + 2,
reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(&net_payload_len));
uint16_t payload_len = ntohs(net_payload_len);
pos += 2;
if (buffer.size() < pos + payload_len + 4) {
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid payload length");
}
packet.payload.assign(buffer.begin() + pos,
buffer.begin() + pos + payload_len);
pos += payload_len;
uint32_t net_checksum;
std::copy(buffer.begin() + pos, buffer.begin() + pos + 4,
reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(&net_checksum));
packet.checksum = ntohl(net_checksum);
uint32_t calculated_cs = std::accumulate(packet.payload.begin(),
packet.payload.end(), 0);
if (calculated_cs != packet.checksum) {
throw std::runtime_error("Checksum verification failed");
}
return packet;
}
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const FiveGDataPacket& pkt)
{
os << "5G Packet ["
<< "Ver: " << static_cast<int>(pkt.protocol_version)
<< ", Type: " << static_cast<int>(pkt.packet_type)
<< ", Timestamp: " << pkt.timestamp
<< ", Payload Size: " << pkt.payload.size()
<< ", Checksum: 0x" << std::hex << pkt.checksum << "]";
return os;
}
private:
static uint64_t ntohll(uint64_t value) {
#ifdef _WIN32
return static_cast<uint64_t>(ntohl(value & 0xFFFFFFFF)) << 32 |
ntohl(value >> 32);
#else
return be64toh(value);
#endif
}
static uint64_t htonll(uint64_t value) {
#ifdef _WIN32
return static_cast<uint64_t>(htonl(value & 0xFFFFFFFF)) << 32 |
htonl(value >> 32);
#else
return htobe64(value);
#endif
}
};
int main() {
#ifdef _WIN32
WSADATA wsaData;
if (WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData) != 0) {
std::cerr << "WSAStartup failed" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
#endif
try {
std::vector<uint8_t> test_data(300, 0xAA);
FiveGDataPacket original(2, 0x1F, 1609459200000, test_data);
auto serialized = original.serialize();
std::cout << "Serialized size: " << serialized.size() << " bytes\n";
FiveGDataPacket reconstructed = FiveGDataPacket::deserialize(serialized);
if (original == reconstructed) {
std::cout << "Operation successful!\n";
std::cout << reconstructed << std::endl;
}
}
catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "Error: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
#ifdef _WIN32
WSACleanup();
#endif
return 0;
}
|
四.总结
1.复习回归:构造函数、容器、拷贝构造函数、运算符重载、static关键字、
2.新学内容:构造函数的初始化列表来初始化成员变量、accumulate(first, last, init)函数、explicit 关键字、移动构造函数、赋值运算符与默认拷贝构造函数的区别、htonll() 函数、htons()、htonll()、htonl()区别、reinterpret_cast<> 介绍、throw 关键字、std::invalid_argument 类、std::invalid_argument 类、输出流运算符(operator<<)
